Importing products—especially from China—can be profitable, but it comes with costs that many businesses overlook. The price you pay your supplier is only one piece of the puzzle. To protect your margins and avoid unexpected expenses, you must understand duties, taxes, shipping fees, and other import charges. Here’s a practical guide to help you calculate accurate landed costs from start to finish.
What is Landed Cost?
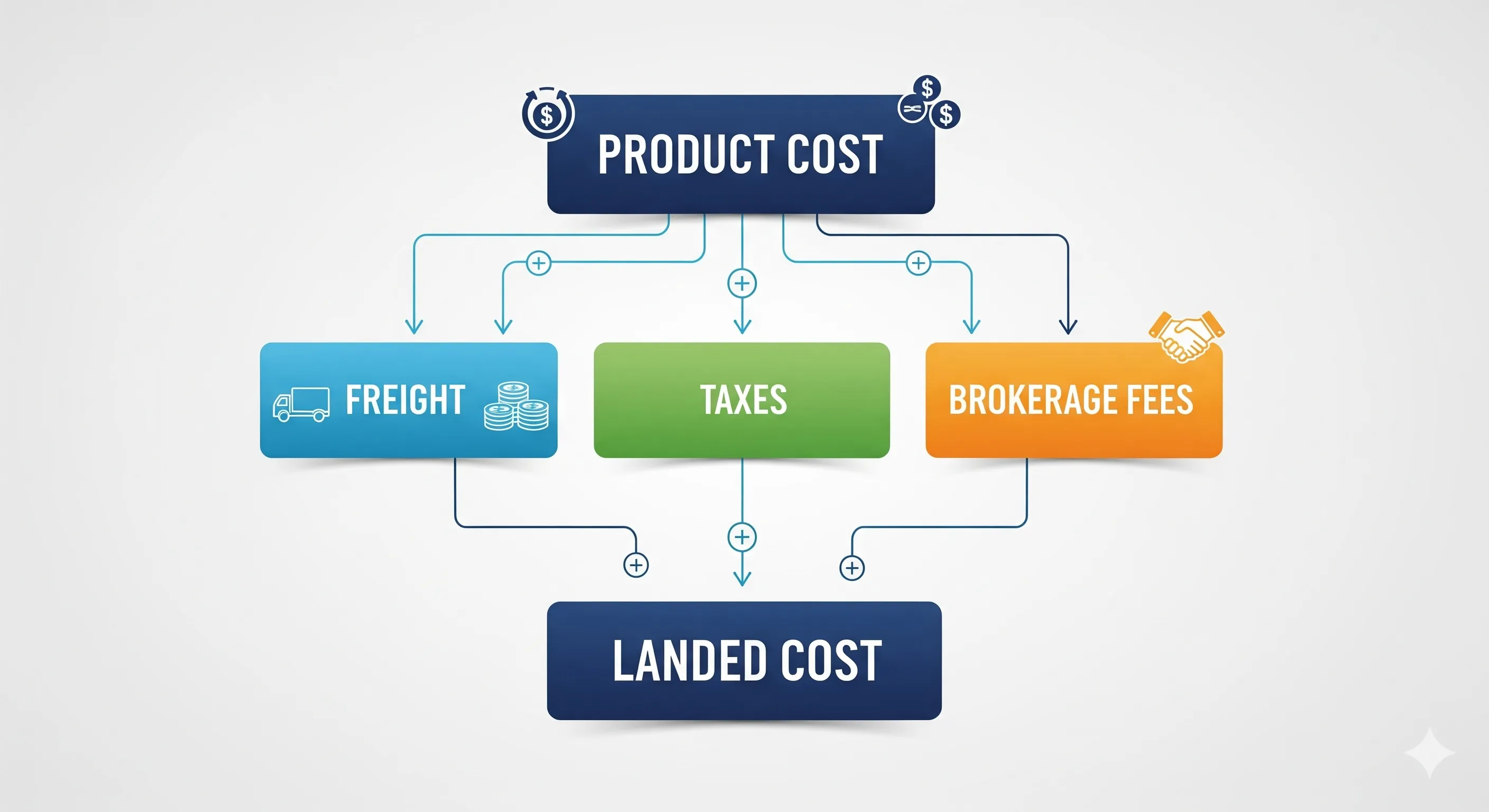
Landed cost is the total cost of getting a product from the manufacturer to your warehouse or customer. It includes:
- Product cost (invoice price)
- Freight (shipping) and insurance
- Import and freight documentation & handling fees
- Customs duty & tariffs
- Any import taxes (VAT, GST, Sales Tax)
- Brokerage, clearance, and inland transport charges
Understanding this total cost prevents profit erosion and helps with better pricing decisions.
- Product invoice value: Base for all calculations
- HS / HTS code: Determines duty rate — incorrect codes can cause extra costs or delays
- Country of origin: Determines eligibility for preferential tariffs
- Destination country: Duty and tax rates vary worldwide
- Incoterm (EXW, FOB, CIF, DDP…): Defines who is responsible for freight, insurance, and risk
- Freight & insurance costs: Required for customs valuation under most tariff systems
- Quantity, packaging, weight: Affects shipping costs and handling fees
- Certificates / permits: Needed for compliance (e.g., FDA, CE, FCC)
Step-by-Step Duty & Tax Calculation
- Find customs value: Usually the product price + freight + insurance (if applicable).
- Determine duty rate: Use the correct HS / HTS code for the product under the destination country’s tariff schedule.
- Calculate import duty: Duty = Customs Value × Duty Rate.
- Add import taxes (VAT/GST/Sales Tax): Tax is generally applied on (Customs Value + Duty).
- Add other charges: Brokerage fees, port handling, document fees, inland delivery charges.
- Compute total landed cost: Add all the above and divide by the number of units to get a per-unit landed cost.
Example Calculation
- Product invoice value: US $5,000
- Freight & insurance: US $500
- Customs value (CIF): $5,500
- Duty rate: 3.5% → Duty = $192.50
- Tax base: $5,500 + $192.50 = $5,692.50
- VAT (20%): $1,138.50
- Total import charges: $1,331.00
Add brokerage and inland delivery to get the final landed cost.
Tips for Accurate Landed Cost Planning
- Classify products correctly: HS/HTS codes drive duty rates — always double-check with your supplier and local customs tariff schedules.
- Model multiple scenarios: Compare costs under EXW, FOB, CIF, or DDP to understand risk and responsibility.
- Check for trade agreements: Preferential tariffs or duty exemptions may reduce your cost if goods meet origin requirements.
- Update regularly: Customs rates, low-value exemptions, and VAT rules can change — always confirm before quoting customers.
- Use cost calculators: Online duty/tax estimators can give quick figures, but confirm with a licensed customs broker for large shipments.

Common Mistakes & How GSW Solutions Helps
- Wrong HS code: Incorrect duty rate, risk of re-classification. We verify and confirm correct classification.
- Ignoring required documents: Delays or loss of preferential tariff. We gather and check all origin certificates and paperwork.
- Forgetting hidden fees: Under-estimated costs and reduced margins. We include all clearance, port, and inland charges.
- Assuming old exemptions still apply: Unexpected duty on arrival. We keep track of policy changes and advise you.
Final Word
When importing goods, your true cost is more than just the supplier’s price. Duties, freight, taxes, and clearance fees all add up. A proper landed cost calculation lets you plan profit margins accurately and avoid costly surprises.
At GSW Solutions, we specialize in helping importers and businesses estimate landed costs, choose the right Incoterms, and manage end-to-end procurement smoothly.
If you want us to calculate duty and tax estimates for your products, please provide the following details:
- Importing From:
- Importing To:
- Product Description:
- Example: “Nike Shoes” or “Electric Guitar”
- OR provide HS Code:
- Product Value:
- Amount: (in currency of origin)
- Product Quantity:
- CIF / Shipping Information:
- Shipping cost: (in currency of origin)
- Insurance cost: (in currency of origin)






